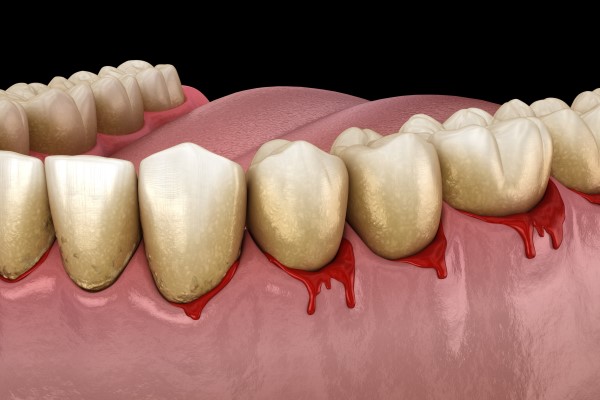
Sometimes oral injuries, intense brushing, and even smoking or chewing tobacco can result in bleeding gums. However, gingivitis is one of the most common causes of bleeding gums. Gingivitis, frequently called gum inflammation, is the initial phase of gum disease that may end in receding gums and tooth loss. Gum bleeding is a condition that cosmetic dental services can address in your area. They can assist with determining the cause of his patient’s bleeding gums and advise the best course of action to prevent further discomfort.
Causes of bleeding gums
Gingivitis can result in the following symptoms in addition to bleeding gums:
- Purple and red gums
- Enlarged and soft gums
- Halitosis, or bad breath
- Plaque formation on the gum line
- Temperature sensitivity of the gums
If you observe any changes in the condition of your gums, get in touch with your dentist. They can assist you in correcting your symptoms and restoring your smile’s health. You can experience significant gum recession, gum pain, and loose teeth if inflammation is not addressed. Early prevention is essential for preventing gum disease or periodontitis.
Treatment
Treatment for bleeding gums depends on the underlying reason. A periodontist (an expert in gum disease) or a dentist can recommend the best course of action if bleeding gums are caused by gum disease.
Common treatments for gum disease include:
- Improved at-home oral hygiene.
- Antibiotics.
- Thorough dental cleaning (tooth scaling and root planing).
- Osseous surgery (to make the spaces around your teeth smaller).
- Periodontal laser surgery.
Brushing and flossing twice daily is the best way to prevent gum inflammation and disease. Before brushing, floss to remove food particles from the gums. Bacteria around the teeth and gums can be removed by brushing twice daily for a minimum of two minutes. To prevent the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth, tooth cleanings and antibacterial rinses can be performed by your dentist. Antibacterial mouthwashes remove oral bacteria and reduce the risk of gum disease.
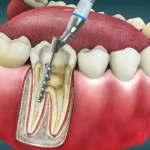
Deep cleaning treatments that remove plaque and tartar from the oral cavity include scaling and root planing. A bacterial coating called plaque is sticky. Without tartar removal, plaque hardens around the teeth and gums. Plaque and tartar are eliminated from the teeth and gums by dentists during a scaling treatment. Root planing eliminates microorganisms to help the tooth roots reestablish the gums.
Laser dentistry or oral surgery is advised for individuals with mild to severe gum disease. These procedures remove the infected gum tissue. Furthermore, they could graft normal gum tissue to the smile’s weaker areas. Make an appointment with your dentist to evaluate your smile and determine the most suitable action for your symptoms.