Recovery from addiction extends beyond detox and therapy—it’s a holistic journey that demands physical, mental, and emotional reinforcement. Among the most impactful yet underutilized tools in addiction recovery are structured exercise and balanced nutrition. These lifestyle interventions not only rebuild the body but also support long-term sobriety and emotional well-being. In early recovery stages, individuals often face depleted energy, mood instability, and disrupted sleep cycles. Integrating movement and nutrient-dense meals helps stabilize these imbalances. When paired with structured addiction treatment in Georgia, physical wellness becomes a powerful ally in preventing relapse and regaining control.
How Exercise Supports the Recovery Process
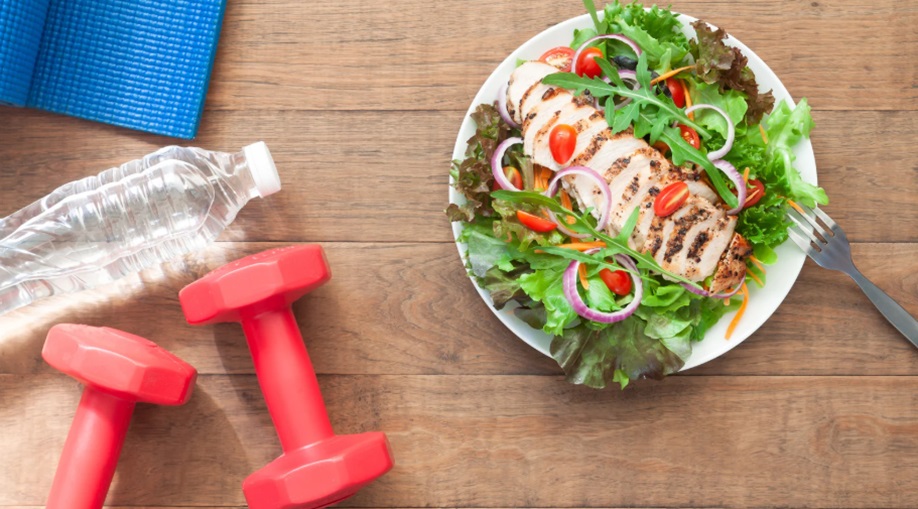
Establishing a consistent fitness routine can significantly influence the success of recovery. Regular physical activity triggers endorphin release—natural chemicals that improve mood and reduce stress. This biological response is especially beneficial for individuals whose brain reward systems have been compromised by substance use. Beyond mood regulation, exercise improves sleep quality, cognitive function, and self-esteem. Activities like swimming, strength training, or even walking can provide structure, distraction from cravings, and a sense of accomplishment. Recognizing the top warning signs of alcohol addiction early, such as increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and neglect of responsibilities, is crucial for initiating timely intervention and support.
Role of Nutrition in Healing the Body and Mind
Poor dietary habits are common among individuals in active addiction. Many substances suppress appetite or alter metabolic processes, leading to vitamin deficiencies and weakened immune function. Recovery is an opportunity to reverse this damage through mindful nutrition. A balanced diet focused on whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables helps restore neurotransmitter production and reduces inflammation. This nutritional rehabilitation improves energy levels and brain function, making it easier to focus on therapy, job responsibilities, or family reintegration. Maintaining blood sugar stability through regular meals also reduces irritability and anxiety, two common relapse triggers. Reinforcing physical health through diet is not just about weight management—it’s about establishing a biological foundation for mental clarity and emotional regulation.
The Synergistic Impact on Mental Health
When exercise and nutrition are integrated into recovery, their effects are amplified. Exercise enhances the body’s ability to absorb nutrients by improving circulation and metabolic efficiency. Meanwhile, proper nutrition supports muscle repair and the stamina needed for consistent physical activity. Understanding the patterns, effects, and treatment options of drug addiction helps in making these lifestyle choices that can help restore brain chemistry and support emotional resilience. In combination, they enhance stress management capabilities, elevate mood naturally, and improve one’s outlook—critical benefits in the face of long-term sobriety challenges.
Conclusion
Rehabilitation must go beyond abstinence. Exercise and nutrition are fundamental to repairing the damage caused by substance abuse, building new habits, and strengthening both physical and mental health. When incorporated as part of a structured recovery program, these tools provide measurable benefits in relapse prevention and long-term wellness. While medical and therapeutic care remains essential, integrating movement and balanced meals can fortify every aspect of recovery, transforming it into a sustainable, health-centered lifestyle.